ERP vs. CRM: Comparison & Benefits
Do you need Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) or Customer Relationship Management (CRM) assistance? These crucial business management systems help organizations streamline operations and improve customer satisfaction. Although they are both (ERP & CRM) software systems, they have different functions and serve other purposes.
In this article, we will examine this closely. ERP and CRM, comparing and contrasting their features, benefits, and use cases.
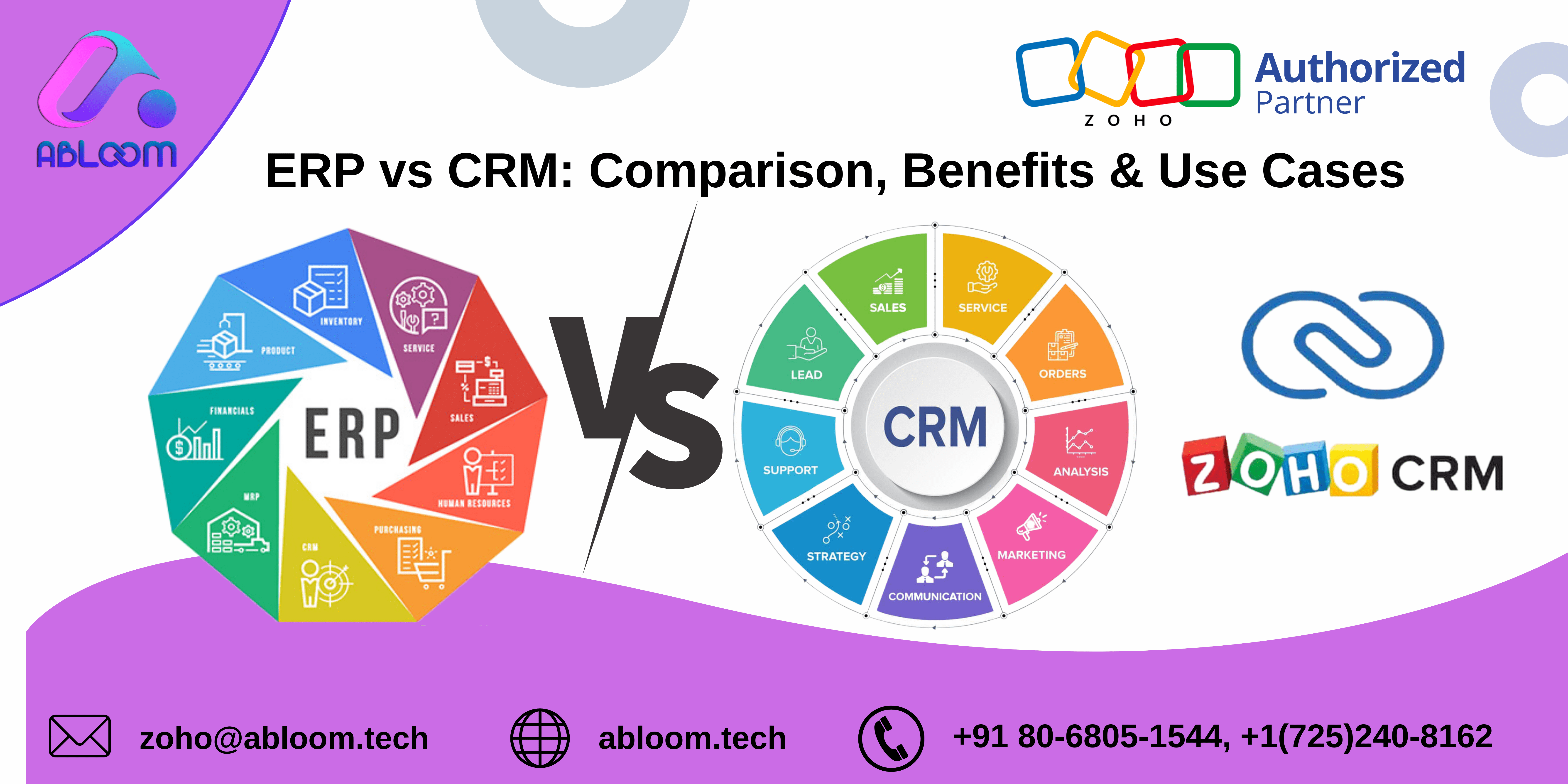
What is ERP?
It is a software system that integrates ERP and all the different functions of a business, including accounting, inventory management, human resources, and customer service, into a single system. This gives companies a comprehensive overview. By improving their operations, they can make more informed decisions.
What is CRM?
However, it is a piece of software. A system specifically designed to manage customer relationships. This includes lead management, contact management, sales management, and customer service. CRM aims to improve customer satisfaction by making customer accounts management easier for businesses—interactions and understanding their needs.
While ERP and Customer Relationship Management have specific functions, they can complement each other and improve a business’s overall performance. For example, an ERP system can be integrated with a CRM system for better inventory management and more accurate customer demand forecasting.
Benefits of ERP & CRM
It’s important to note that while both systems can streamline business processes and improve efficiency, they are not interchangeable and are best used for their intended purposes.
Differences between ERP and CRM
After learning both the terms and their benefits, let’s take a quick view at their differentiating factors:
Features:
(Data Management)
ERP: ERP systems provide a comprehensive view of a company’s internal operations and resources, financial data, inventory, and production schedules. They allow data integration across different departments and locations, providing a centralized data repository.
CRM: CRM systems provide a comprehensive view of customer interactions and relationships, including customer data, sales history, and communication records. They allow for tracking and analyzing customer interactions, providing valuable insights for sales and marketing strategies.
(Functionality)
ERP: ERP systems typically include modules for financial management, inventory management, human resources, and production planning. They are designed to automate and streamline internal processes and operations, improving efficiency and data accuracy.
CRM: CRM systems typically include modules for sales management, marketing automation, and customer service. They are designed to manage customer interactions and relationships, providing tools for lead management, customer segmentation, and campaign management.
Use Cases
Regarding use cases, ERP is more suitable for larger organizations with multiple departments and the need to manage various business functions. It is also helpful for businesses with a lot of data and needs to make sense of it.
On the other hand, CRM is more suitable for businesses with many customer interactions and needs to manage these interactions more efficiently.
ERP vs. CRM Different
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) and CRM (Customer Relationship Management) are software systems businesses use to manage their operations. While they serve different purposes, they can complement each other and are often integrated to provide a comprehensive solution. Here’s a breakdown of ERP and CRM:
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning):
- Function: ERP systems are designed to streamline and integrate various business processes and procedures across an organization. They typically include modules for finance, human resources, manufacturing, supply chain management, inventory management, procurement, and more.
- Key Features: ERP systems provide a centralized database and real-time access to information, enabling efficient data management, automation of business processes, and standardized workflows.
- Benefits: ERP helps improve operational efficiency, reduce manual tasks, eliminate data silos, enhance collaboration, and provide accurate insights for decision-making. It enables businesses to manage resources effectively and optimize overall performance.
CRM (Customer Relationship Management):
- Function: CRM systems are focused on managing and nurturing customer relationships. They provide tools to track interactions, manage leads, automate sales processes, and enhance customer service.
- Key Features: CRM systems offer valuable tools like contact management, lead management, opportunity management, sales forecasting: customer service and support, marketing automation, and analytics.
- Benefits: CRM helps businesses improve customer engagement, enhance sales effectiveness, increase customer satisfaction, and drive revenue growth. It enables companies to track customer interactions, manage sales pipelines, and provide personalized experiences.
While ERP and CRM serve different purposes, they can be integrated to offer a more complete perspective. This integration allows for seamless data flow between departments, such as sales, marketing, finance, and production, ensuring consistent and accurate information across the organization. For example, sales teams can access customer data from the CRM system while viewing inventory information from the ERP system to provide accurate delivery estimates.
ERP manages internal business processes and resources, while CRM is dedicated to working customer relationships and interactions. Both systems play critical roles in enhancing business efficiency and profitability, and their integration can provide a holistic view of operations and customers for better decision-making.
Is ERP or CRM best for you?
The choice between ERP and CRM depends on an organization’s needs and goals, including personal preferences or requirements for enterprise resource planning (ERP) or customer relationship management (CRM) systems.
ERP systems are created to manage and integrate. Various business processes include finance, human resources, supply chain management, and manufacturing. They provide a centralized database, help streamline operations, improve efficiency, and enhance collaboration across different departments.
On the other hand, CRM systems focus on managing customer relationships, sales, and marketing activities. They help organizations track customer interactions, drive leads and opportunities, and improve customer service. CRM systems are precious for businesses relying heavily on customer engagement and sales processes.
Organizations may often benefit from implementing ERP and CRM systems, as they serve different purposes. ERP provides a comprehensive view of business operations, while CRM focuses on managing customer relationships and driving sales. Integrating the two systems can enhance data sharing.
Ultimately, the choice between ERP and CRM depends on your organization’s needs and priorities. Evaluating your business requirements, processes, and goals is essential to determine which system or combination will best meet your needs. Consulting with experts or conducting a thorough analysis of your organization’s needs can help you make an informed decision.
Conclusion
We hope you must have understood how both systems can work together to provide a complete and efficient management solution for a business. But if you are an organization, you must assess your specific needs (including the size and nature of the organization, its data, and its customers) before choosing the best and the right system. We at Abloom Technocrats provide world-class CRM Services and are a Zoho-authorized partner.